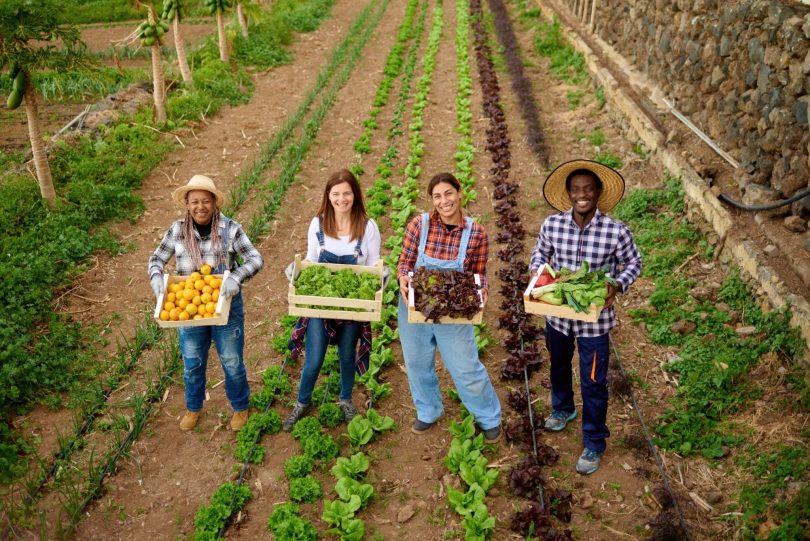
Organic farming plays a pivotal role in promoting health, environmental sustainability, and economic stability, offering a multitude of benefits. By embracing natural agricultural methods, this significantly reduces the use of harmful chemicals, improving soil fertility and biodiversity, which, in turn, enhances the nutritional content of the food produced. As consumer awareness grows, the demand for organic products continues to rise, influencing market dynamics and prompting innovations that aim to address the scalability and efficiency of organic practices, as discussed by Mary Carroll Murphy.
Contents
Essentials of Organic Farming
Organic farming stands apart from traditional agricultural methods primarily because it refrains from using synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, opting instead for natural substances and processes. This form of agriculture relies heavily on techniques such as crop rotation, composting, and biological pest control, which not only reduce chemical run-off but also enhance soil fertility and biodiversity.
The journey from farm to consumer’s table involves various stages, each adhering to strict standards set by certifying bodies. These standards ensure that the integrity of organic produce is maintained throughout the process, from seed selection and cultivation to harvesting and distribution.
In the context of today’s heightened environmental awareness, organic farming presents itself as a sustainable alternative that supports the well-being of our planet. It helps maintain ecological harmony, making a significant contribution to mitigating the ongoing challenges of climate change and biodiversity loss. Through these efforts, organic farming not only provides healthier food options but also plays a crucial role in preserving our environment for future generations.
Nutritional and Environmental Benefits
Organic foods often boast higher levels of nutrients compared to their conventionally grown counterparts. Numerous studies indicate that organic produce tends to contain more vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which are crucial for maintaining good health. This nutritional enhancement can be attributed to the methods used in organic farming, which improve the soil’s quality and, in turn, affect the nutritional content of the crops.
The environmental benefits of organic farming are just as significant. This form of agriculture minimizes the farmer’s carbon footprint by reducing dependency on chemical inputs and fossil fuels. Moreover, organic farming practices enhance soil structure and water filtration, helping to prevent harmful runoff and preserve local water sources. These practices also encourage biodiversity, including a healthier pollinator population, which is vital for the growth of many crops and the health of ecosystems.
Health Advantages
Choosing organic foods can reduce the intake of pesticides and other potentially harmful chemicals commonly used in conventional agriculture. This is vital for groups like children and pregnant women whose health could be adversely affected by such substances. Lower pesticide exposure is linked to a decrease in health risks such as birth defects, obesity, and even certain cancers, according to several studies.
Further supporting the case for organic foods are the findings that link organic diets with improved immune system status and better metabolic health. As more consumers become aware of these health benefits, the preference for organic products continues to rise, influencing a broader shift towards organic options in the general population.
Economic and Market Dynamics
The economic landscape of organic farming is characterized by both higher production costs and higher market prices compared to conventional farming. These costs are often due to the more labor-intensive methods of organic farming and the stringent certification processes required to label products as organic. Despite these challenges, the market for organic products is expanding rapidly, driven by consumer demand for healthier and environmentally friendly products.
Current Challenges and Efforts
One of the main hurdles facing organic farming today is the scalability of its practices. The labor-intensive nature of organic methods, coupled with the need for specific knowledge and skills can make large-scale production challenging. Moreover, there are widespread misconceptions about organic farming that hinder its acceptance. Addressing these challenges involves a concerted effort to educate the public and stakeholders about the benefits of organic farming. Through educational campaigns and outreach programs, misconceptions can be corrected, and more accurate information can be spread, facilitating a better understanding and wider adoption of organic practices.
Prospects and Innovations in Organic Farming
Looking to the future, innovations in technology and farming practices promise to enhance the efficiency and reach of organic farming. Advances such as precision agriculture, which uses technology to optimize the timing and application of inputs, can help organic farmers achieve greater yields and reduce their environmental impact.
Additionally, the development of new organic pesticides and fertilizers that are more effective and less costly could also prove pivotal in addressing the current limitations of organic farming. As these technologies and practices evolve, they hold the potential to influence the sustainability and productivity of organic agriculture, ensuring its viability as a solution for food security and environmental conservation.