Supply chain disruptions is a term that has become part of the economic terminology. The movements of raw materials and final goods have driven up prices across the globe. The increase in intermediate goods has been driven by the pandemic as well as excess liquidity, such as accommodative monetary policy. While some producers of raw materials benefit from higher prices, most consumers suffer. The upshot is higher commodity trading of raw materials spills over into the cost of final goods. For example, higher crude oil prices usually lead to higher gasoline prices. When the price of raw materials rises too quickly, central banks typically get involved and tighten monetary policy to reduce demand and mitigate the impact of higher raw material prices. The net effect is generally a slowdown in growth.
Contents
What has Driven up the Price of Raw Materials?
The impetus for rising raw material prices during 2021 and the beginning of 2022 has been a combination of factors. The pandemic has been a significant reason for the rapid increase in raw material prices. An example of this wild rise occurred in the oil arena, as lockdowns were implemented across the globe and the demand for gasoline and jet fuel created from crude oil declined rapidly. To offset this sharp drop in demand for oil, producers cut supply. Commodity trading of oil prices tumbled as the market dropped.
After dropping to the lowest levels on record (commodity trading of WTI crude oil fell below zero), prices stabilized and started to rally once vaccines were introduced. As travel demand started to accelerate, as lockdowns lifted, oil prices rose. The oil supply could not keep up with the need for end products like gasoline. When demand increases and supplies are limited, the cost of the raw material is forced higher.
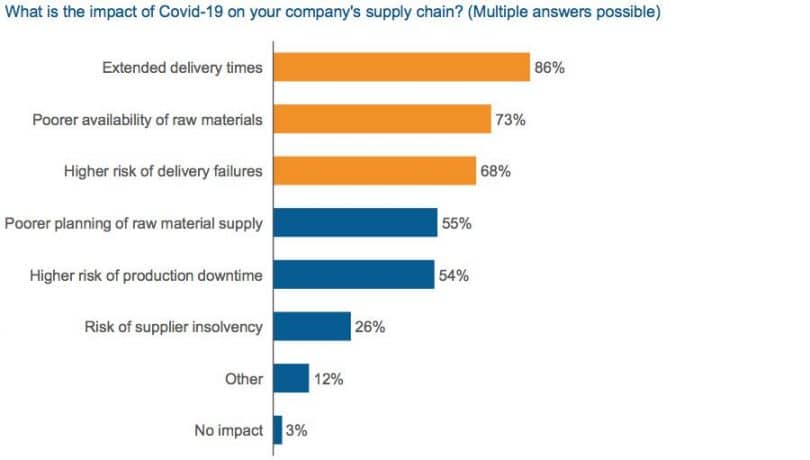
Alt Text: Extended delivery times and lower raw material availability are the biggest challenges for the supply chain.
https://www.consultancy.eu/news/7143/raw-material-prices-and-supply-shortages-skyrocket-in-7-charts
Transportation of Materials is Impacted
The pandemic significantly impacted the production of raw materials. Additionally, the transportation of raw materials was hampered. During the lockdown, the decline in demand for raw materials left vessels and containers in random places worldwide. Suppliers who were called on to increase the production of raw materials could not ship them to the locations where demand had accelerated. Even if supplies were available and demand was strong in another area, the price would rise without the proper infrastructure available to ship these materials. In the United States, shipping goods by truck or rail increased by 23% year over year. Trucking rates also increased because of the lack of truckers available to drive trucks. Shippers rushed to find individuals who would come back to work quickly to help the supply chain process and they also needed to increase the wages they were offering. The combination of higher shipping rates and salaries is incorporated into the raw materials’ final delivered price.
How Do Higher Raw Material Prices Impact Economic Growth?
The combination of reduced supply and higher transportation costs with accommodative monetary and fiscal policy leads to higher prices. The U.S. Federal Reserve cut its benchmark interest rates to zero to offset the drop in demand. The increase of liquidity allowed money to change hands at an accelerated rate, which assisted in driving up prices. With raw material prices at unsustainable levels, the Fed is now set to reverse its accommodative policy stance. Market pundits now believe the Fed will increase interest rates in March of 2022. Raising rates and reducing monetary policy will help eliminate liquidity and reduce demand. Unfortunately, if the supply chain disruptions persist, transportation costs will remain elevated. As the Fed increases interest rates, the net impact will reduce growth. Even with increased interest rates, the Fed Funds rate will remain historically low. Despite the depressed levels of Fed Fund rates, higher rates should decelerate growth patterns in the wake of higher raw materials.
The Bottom Line
The effect of higher raw materials eventually will hurt growth. While higher raw material prices can help the producers of raw materials, the consumer ultimately pays the price. Higher raw material prices usually bleed into consumer goods. Additionally, transportation costs play a role in the delivered price of raw materials. The whipsaw economic activity seen moving away from lockdowns has created instability in raw materials. It has been very difficult to get people to come back to work. Initially, the fiscal stimulus offered by governments discouraged people from coming back to work. As demand grew, the need for employees has pushed wages higher, allowing people to purchase goods that have increased in price. The upshot is that accelerated raw materials prices will need to be addressed with tighter monetary policy. Higher interest rates could eventually take their toll on growth and potentially cause an economic recession.